Maharaja Jagatjit Singh of Kapurthala: A Visionary Global Influencer
Introduction
Maharaja Sir Jagatjit Singh of Kapurthala was one of the most remarkable monarchs in Indian history, renowned for his progressive outlook, diplomatic skills, and love for European culture. As the last ruling Maharaja of Kapurthala, he played a significant role in shaping the state’s modernization while maintaining its rich heritage. His contributions to architecture, education, and foreign relations continue to inspire historians and scholars today.
Early Life and Ascension to the Throne
Born on 24 November 1872, Maharaja Jagatjit Singh belonged to the Ahluwalia dynasty, a prominent ruling family of Punjab. He ascended the throne in 1877, following the demise of his father, Maharaja Kharak Singh, at a young age. Due to his tender age, a regency council managed state affairs until he assumed full administrative control in 1890.
Despite the responsibilities of rulership, Maharaja Jagatjit Singh received a refined education that emphasized political strategy, governance, and diplomacy. His exposure to European ideals deeply influenced his governance and vision for Kapurthala’s future.
A Patron of Architecture and Art
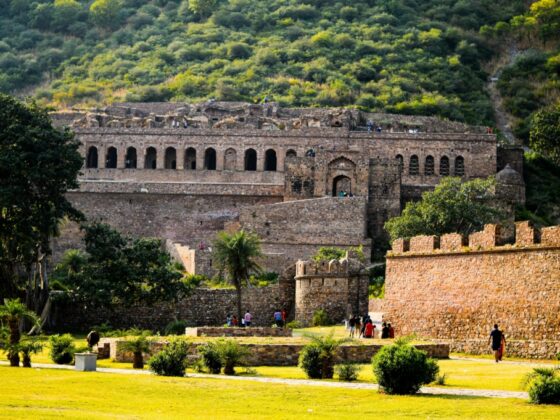
Maharaja Jagatjit Singh’s passion for European culture manifested in the grand architectural projects he undertook. Inspired by his travels to France, he transformed Kapurthala into a city that mirrored Parisian elegance. Some of his most notable contributions include:
1. Jagatjit Palace
The Jagatjit Palace, built in 1908, stands as a magnificent example of Indo-European architectural fusion. Designed by French architects, the palace reflects the Beaux-Arts style, featuring exquisite marble work, domed ceilings, and grand chandeliers. Today, it serves as the Sainik School of Kapurthala.
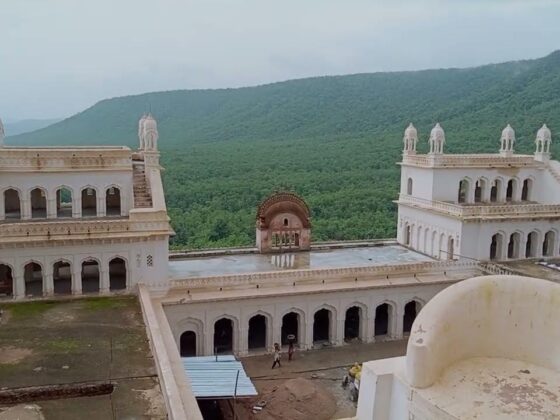
2. Elysee Palace and Moorish Mosque
Another architectural marvel inspired by European influences is the Elysee Palace, designed as a luxurious retreat for the Maharaja. He also commissioned the Moorish Mosque, modeled after the Grand Mosque of Marrakesh, reflecting his admiration for global cultures and architectural styles.
3. Jagatjit Club and Clock Tower
To promote cultural and intellectual exchange, he established the Jagatjit Club, an elite social gathering venue. The Clock Tower, another iconic structure, symbolizes Kapurthala’s transformation into a modern princely state.
Foreign Relations and Travels
Maharaja Jagatjit Singh was a globetrotting monarch, extensively traveling across Europe, America, and the Middle East. His diplomatic engagements included meetings with world leaders such as:
- King George V of England
- President Theodore Roosevelt of the United States
- French and Italian Nobility
His extensive travels enriched his knowledge and facilitated alliances that benefited Kapurthala. He was a vocal supporter of Indian autonomy within the British Empire, advocating for princely states’ progressive reforms.
Education and Social Reforms
Recognizing the power of education in nation-building, Maharaja Jagatjit Singh prioritized modern schooling and higher education. He established several institutions, including:
- Jagatjit High School – A premier educational institute in Punjab.
- Kapurthala State Library – A hub for literature and research.
- Scholarship Programs – Encouraging students to study abroad.
His progressive approach extended to social reforms, including women’s education, healthcare, and infrastructural development.
Role During British Rule and Indian Independence
As a ruler under British India, Maharaja Jagatjit Singh maintained cordial relations with the British Crown. He represented India at the League of Nations in 1927, a rare honor for an Indian prince. Additionally, he attended the First Round Table Conference (1930), where he expressed his vision for India’s future.
Despite his loyalty to the British, he gracefully integrated Kapurthala into independent India in 1948, when princely states were merged into the Indian Union.
Personal Life and Interests
Maharaja Jagatjit Singh led a lavish yet cultured lifestyle. He was an ardent lover of French fashion, classical music, and literature. His extravagant collections included vintage cars, precious jewels, and European artworks.
He married several times, with his most famous consort being Anita Delgado, a Spanish flamenco dancer who became Princess Prem Kaur after marriage. Their love story fascinated many and remains a subject of historical interest.
Legacy and Death
Maharaja Jagatjit Singh passed away on 19 June 1949, marking the end of an era. His legacy, however, continues to thrive through:
- The preserved architectural wonders of Kapurthala.
- His contributions to education and social reforms.
- His impact on diplomatic and cultural relations.
Today, Kapurthala remains a symbol of his progressive leadership and artistic vision, attracting history enthusiasts, tourists, and architects from around the world.
Conclusion
Maharaja Sir Jagatjit Singh of Kapurthala was more than just a ruler; he was a visionary who embraced modernity while respecting tradition. His love for art, architecture, and diplomacy shaped Kapurthala into one of India’s most unique princely states. His legacy continues to inspire, serving as a testament to his forward-thinking approach, global influence, and cultural contributions.
Whether you are an admirer of royal history, architectural elegance, or diplomatic brilliance, Maharaja Jagatjit Singh’s life remains a fascinating tale of grandeur, intellect, and visionary leadership.








